Graph Of Yx2 Transformations
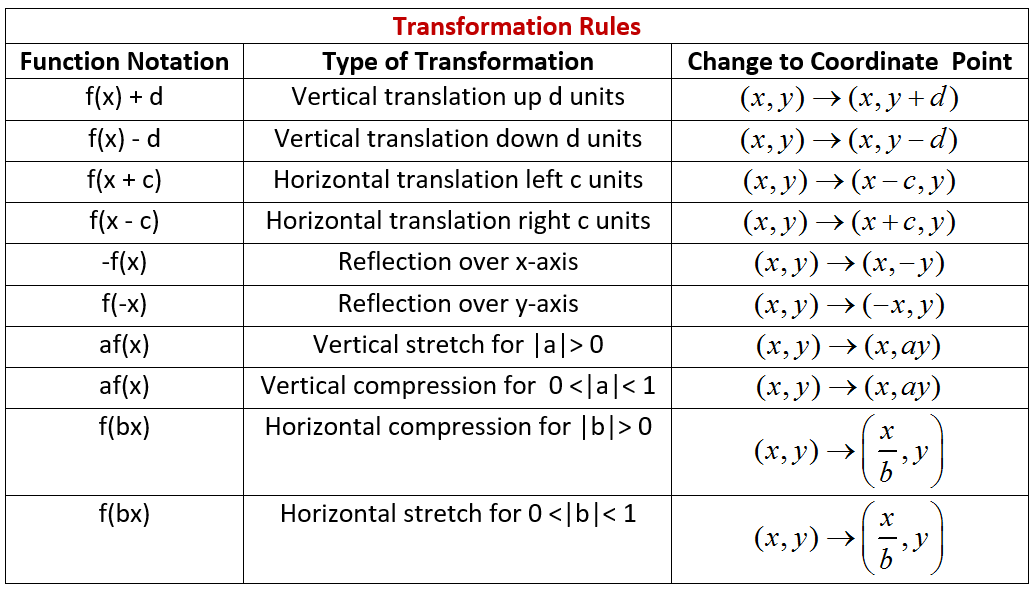
H is the horizontal shift.
Graph of yx2 transformations. Asked by beatrize on December 11, 12;. The basic graph is exactly what it sounds like, the graph of the basic function. For instance, the graph for y = x 2 + 3 looks like this:.
Sometimes graphs are translated, or moved about the. Here we are going to see, how to graph the function using transformations. In this case, which means that the graph is not shifted to the left or right.
How did we transform from y=x 2?. Is a rigid transformation that shifts a graph up or down relative to the original graph. Shifted up five units.
Use the graphs of f and g to describe the transformation from the graph of f to the graph of g. G(x) = x 2 + C. Graphing Transformations Use the graph of y = x2 in Figure 4.
- The graph is shifted to the right units. Determine whether a function is even, odd, or neither from its graph. Y = 1 __ 3 x 2 3.
Use the technology to graph each of the functions. Sketch, on separate diagrams, the graphs of. Figure232 shows the graphs of \(f (x) = x^2 + 4\text{,}\) \(g(x) = x^2 - 4\text{,}\) and the basic parabola, \(y = x^2\text{.}\) By comparing tables of values, we can see exactly how the graphs of \(f\) and \(g\) are related to the basic parabola.
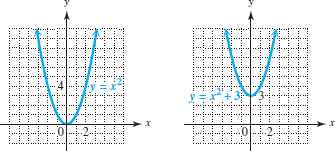
Answer to Use transformations to sketch the graph of the function.y = x2 – 2x + 2. Y =-x 2 + 4 8. Problem 23E from Chapter 2.6:.
G(x) = (x+C) 2. It's a common type of problem in algebra, specifically the modification of algebraic equations. Identify the transformation from the graph of f(x)=x 2 to the graph g(x)= x 2 - 5.
Certain mathematical expressions allow you to combine stretching, shrinking, translating, and reflecting a function all into one graph. C < 0 moves it down We can move it left or right by adding a constant to the x-value:. An expression that shows all the transformations in one is where a is the vertical transformation.
State the domain and range. To find the transformation, compare the two functions and check to see if there is a horizontal or vertical shift, reflection about the x-axis, and if there is a vertical stretch. Write the steps to obtain the graph of the function y = 3(x − 1) 2 + 5 from the graph y = x 2.
For instance, f(x) = –2(x – …. Be sure to graph all of the stages on one graph. Graph the parabola, y =x^2+1 by finding the turning point and using a table to find values for x and y.
A vertical translation A rigid transformation that shifts a graph up or down. How does the graph of y = a(x - h)2 + k change if the value of h is doubled?. Asked by michelle on April 2, 13;.
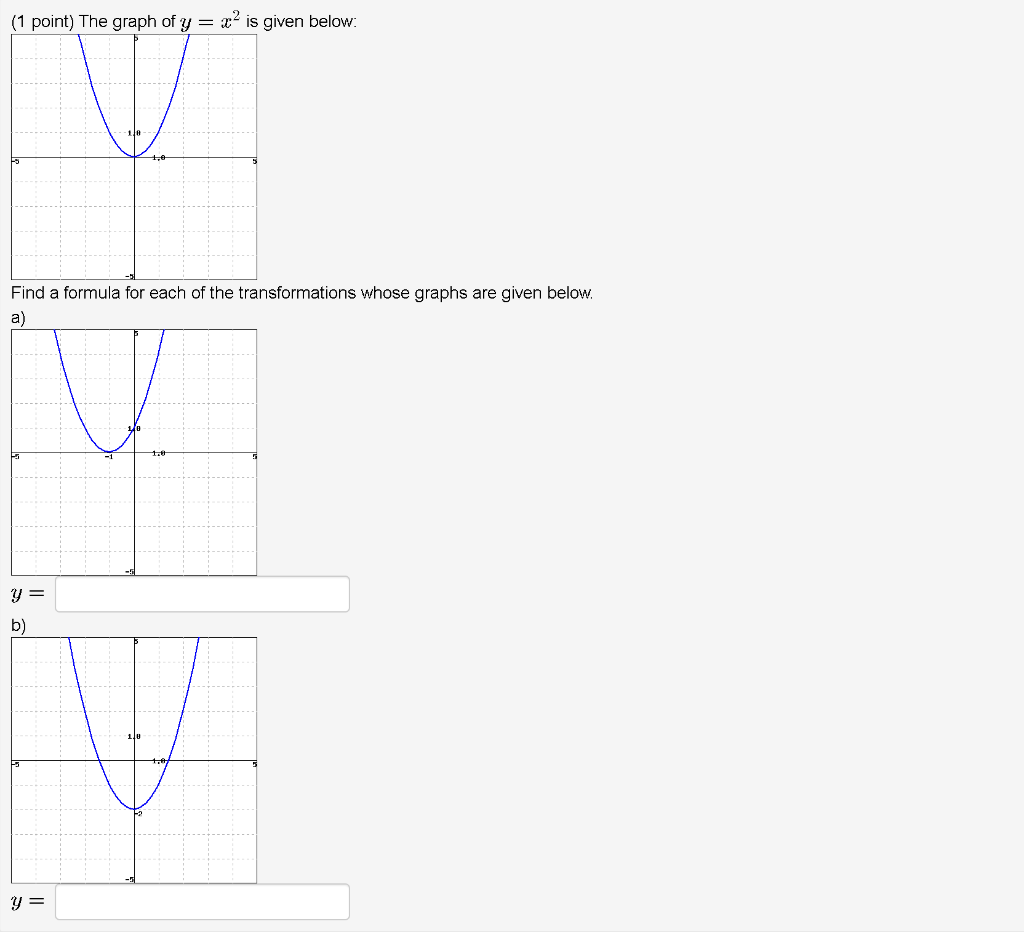
Th en graph each function. There are a number of. Y = x 2 + 2.
This occurs when a. Graph transformation is the process by which an existing graph, or graphed equation, is modified to produce a variation of the proceeding graph. College Algebra (7th Edition) Edit edition.
To visualize how the graph moves, rewrite y = (x - 3)^2 + 4 so that it is easier to compare with y = x^2. P (x) = x 2. Y =-3 x 2 + 5 Write the equation of the function described by each of the.
To obtain each function, identify the transformations that need to be applied to the graph of the parent function y = x 2. Learn algebra 2 transformations graphs with free interactive flashcards. In the picture below, the graph of y = x2 is again a thick black curve;.
State domain and range of each in interval notation. Now you can see that the transformation changed y to (y' - 4) and x to (x' - 3). A transformation takes a basic function and changes it slightly with predetermined methods.
A non-rigid transformation A set of operations that change the size and/or shape of a graph in a coordinate plane. Reflection and horizontal compression. Therefore, the graph of y- 2 2 = 2x is the graph of y= x translated vertically 2 units up.
P(x) = x 2 Transformation:. The graph of y = x2 is called the parent graph for the family of parabolas because every other parabola can be seen as a transformation of that one graph. This isn’t a lesson plan but the ideas here could easily be used in lessons;.
- The graph is shifted to the left units. There are several types of graph transformations. Y = -3x 2.
Y = x 2-8 5. The equation y = (x-8)² + 5 moves the parent function y = x 2 right 8 units and down 5 units. The figure below shows triangle A B C reflected across the line y = x + 2.
Y= -2 lxl +2 For example, if you were asked to graph y= x^2 + 1 using transformations, you would. Given the graph of a common function, (such as a simple polynomial, quadratic or trig function) you should be able to draw the graph of its related function. Give the formula of a function based on its transformations.
Graph functions using a combination of transformations. When we move the graph of the equation y = x 2 down 7 units, we will get the graph with the equation. Precalculus (7th Edition) Edit edition.
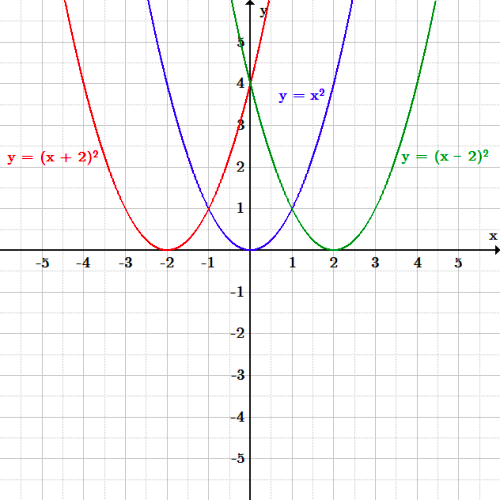
Each point (x, y) on the graph of y= x2 is transformed to become the point (x + 5, y) on the graph of y= (x - 5)2.In mapping notation, (x, y) → (x + 5, y).Therefore, the graph of y= (x - 5)2 is the graph of y= x2 translated horizontally 5 units to the right. Y = y' - 4 ----> y' = y + 4. 1.R - Use transformations to sketch the graph of the.
The graph of y = x2 and y = (x 2)2 Graphs of y = x2 (thick black curve), y = (x 2)2 (thin blue), If instead we multiply the input variable x by a constant, we will contract (shrink) the graph in the horizontal direction. When we move the parent function y = x 2 to the right 8 units, we will have the equation y = (x. Y = x 2 + 10 4.
For a better explanation, assume that is and is. The basic graph will be used to develop a sketch of the function with its transformations. Describe the Transformation y=x^2 The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given.
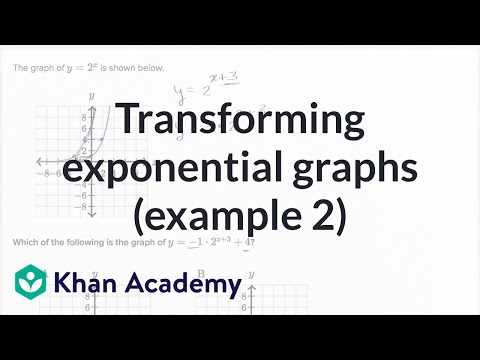
Start studying Transformations of y=f(x). The graph of y = x2 + 3 is the graph of y = x2 shifted upward three units. The graph cuts the y-axis at the point Q and the x-axis at the points ( ±3, 0) and R.
The graph of y = (2x)2 is the. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Shifted down five units.
By graphing the curve y = x 2, we get a open upward parabola with vertex (0, 0). We can move it up or down by adding a constant to the y-value:. Y = -x 2 - 5.
Horizontal stretch by 3. For example, if you were asked to graph y= x^2+11 using transformations, you would show the graph of y = x^2 and the graph. This is a vertical shift.
X y-4 4 4-4-8 8 y = -x2 y = x2 + 3 y = x2. Using Desmos – Transformations of Graphs By Mark Dawes (January 19) If you are new to Desmos you might want to read my earlier blog Desmos – the basics first. Play this game to review Algebra I.
The transformation is shown below. The vertex of the graph moves to a point twice as far from the y-axis. Shift the graph to the right by 2 units, and we will get our desired graph as:.
Changes the size and/or shape of the graph. To move the line down, we use a negative value for C. A vertical translation 4 units up.
The four main types of transformations are translations, reflections, rotations, and scaling. Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graph:. A graph is just a set of points that satisfy an equation That means you can always check your work by plugging in an x-value (I recommend x=0, and seeing if the y-value fits the y-value.
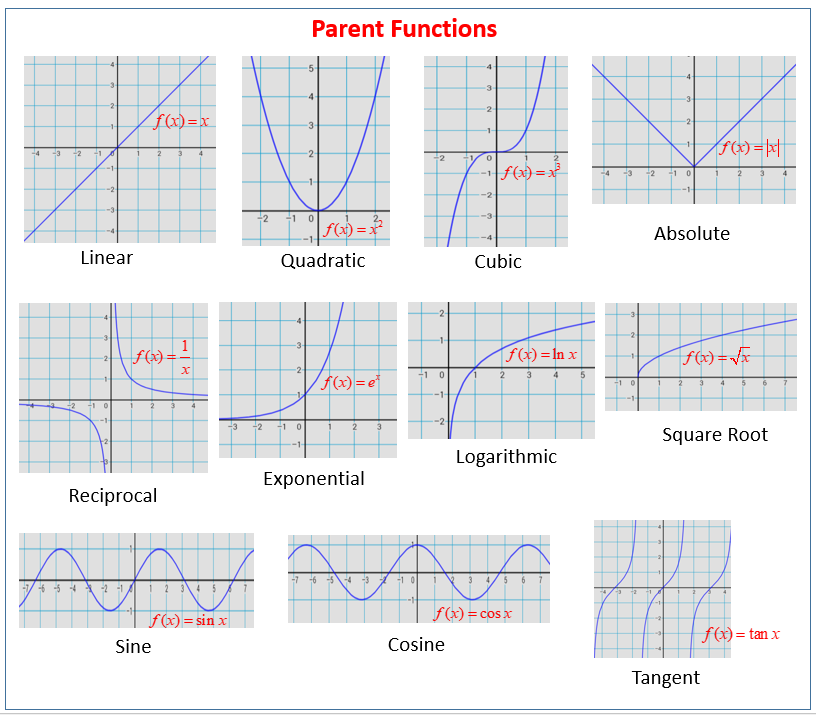
The graphs of many functions are transformations of the graphs of very basic functions. For different values of the constants \(k\) and \(h\text{.}\) Such variations are called transformations of the graph. Graph the following function using transformations.
Shifted left five units. Left 4 up 7. The graph of y = x-2 3.
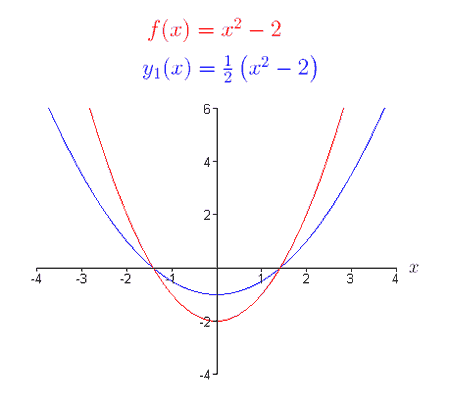
The graph of y = -x2 is the reflection of the graph of y = x2 in the x-axis. V is the vertical shift. The graph of {eq}y=x^2-2 {/eq} is the same as the graph of {eq}y=x^2 {/eq} except that it is shifted vertically down by 2 units.
A third type of transformation is the reflection. C > 0 moves it up;. (y' - 4) = (x' - 3)^2.
We can all see these transformations by looking at the changes in the function. The vertex of the graph moves to a point twice as far from the x-axis. The basic graph can be looked at as the foundation for graphing the actual function.
For the basic function, () =, its basic graph is just a parabola. Learn functions chapter 3 1 transformations with free interactive flashcards. (Again, you can check this by plugging in the coordinates of each vertex.).
Y = 1 __ 2 x 2 + 3 7. This change will cause the graph of the function to move, shift, or stretch, depending on the type of transformation. Problem 23E from Chapter 2.6:.
X = x' - 3 ----> x' = x + 3. Choose from 500 different sets of functions chapter 3 1 transformations flashcards on Quizlet. 2D 3 OLD day 4 Transformations Online ANS.notebook 6 April 02, The role of "h" y=a(xh)2+k 1.
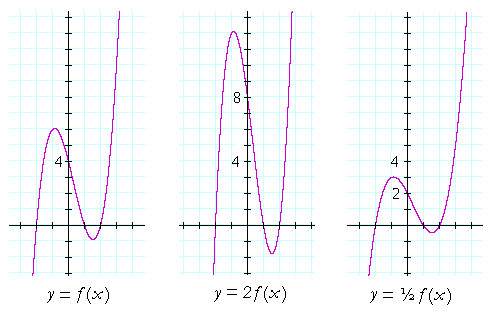
Y = 5 x 2 2. Graphing Transformations Use the graph of y = x2 in Figure 4. Transformations of Graphs ww w.n aike rm at hs.co m 5.
Which transformation transforms the graph of f(x) = x 2 to the graph of g(x) = (x + 4) 2 ?. Describe transformations based on a function formula. Graph the following function using transformations.
Graph functions using a single transformation. True or False ?. Be sure to graph all of the stages on one graph.
Which transformation transforms the graph of f(x) = x 2 to the graph of g(x) = (x + 4) 2?. Figure 1 Figure 1 shows the graph of y = f( x), x J , The graph consists of two line segments that meet at the point P. This reflection can be described in coordinate notation as ( x , y ) → ( y − 2 , x + 2 ).
To find the transformation, compare the two functions and check to see if there is a horizontal or vertical shift, reflection about the x-axis, and if there is a vertical stretch. 1.R - Use transformations to sketch the graph of the. 1.2 Transformations and Parent Graphs Accurately graph the parent function p(x).
Gr.11 - Rational functions graphing. Choose from 500 different sets of algebra 2 transformations graphs flashcards on Quizlet. C is the horizontal transformation.
Y = x 2 - 7. Then graph f(x) as described by a transformation of the parent graph. A function transformation takes whatever is the basic function f (x) and then "transforms" it (or "translates" it), which is a fancy way of saying that you change the formula a bit and thereby move the graph around.
We start with y = x 3. Reflection and vertical stretch. Which could be the equation for g(x)?.
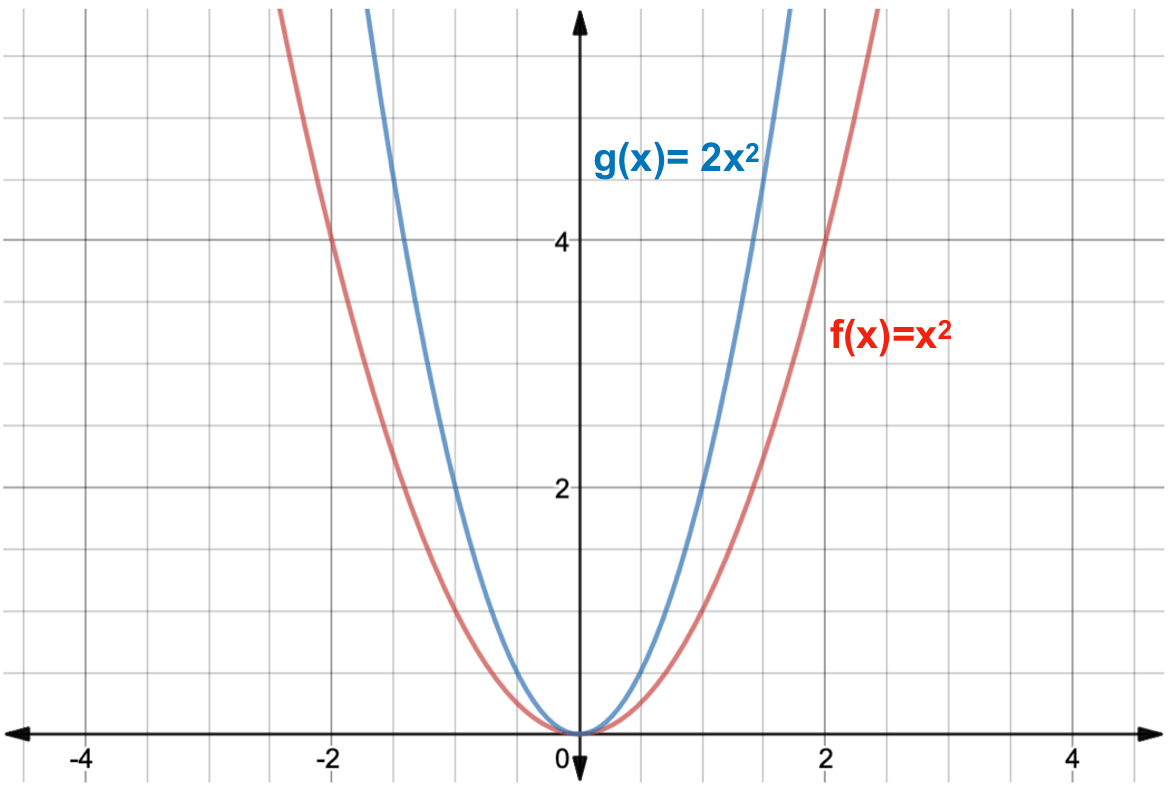
The graph shows the function f(x)=x 2 in blue and another function g(x) in red. This means that the new y' is the old y shifted up 4. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.
These are compression, reflection, stretch, and translation. State the domain and range. Y = 2 x 2-1 6.
The vertex of the graph moves to a point half as far from the x-axis. 3.6 Graphing Transformations You have learned how to move a parabola around a set of axes, write equations, sketch graphs, and model situations.
1 5 Shifting Reflecting And Stretching Graphs
Transformations Of Functions Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
Transformations Of Quadratic Functions College Algebra
Graph Of Yx2 Transformations のギャラリー
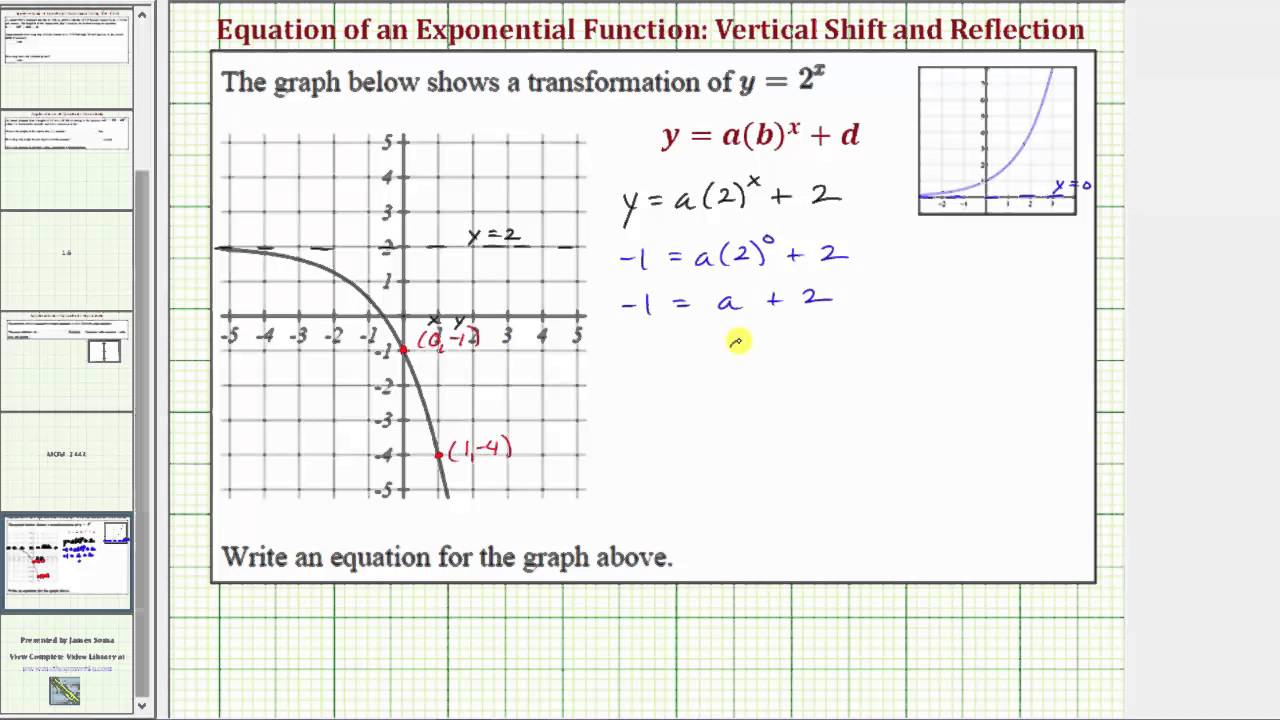
Ex Determine The Equation Of A Transformation Of Y 2 X Youtube

Transformations Mrs F X

Vertical And Horizontal Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation
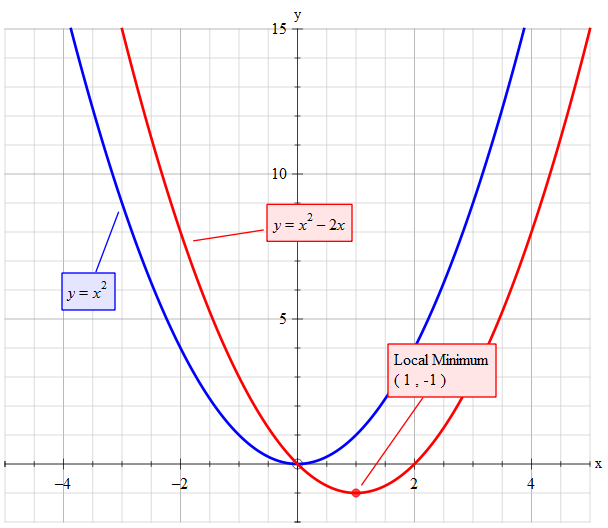
How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2x And Describe The Transformation Socratic

Solved Describe How The Graph Of Y X 2 Can Be Transform Chegg Com
Solution The Graph Of Y X 2 Undergoes A Transformation A Scaling With Scale Factor 2 Along The X Axis What Is The Resulting Graph
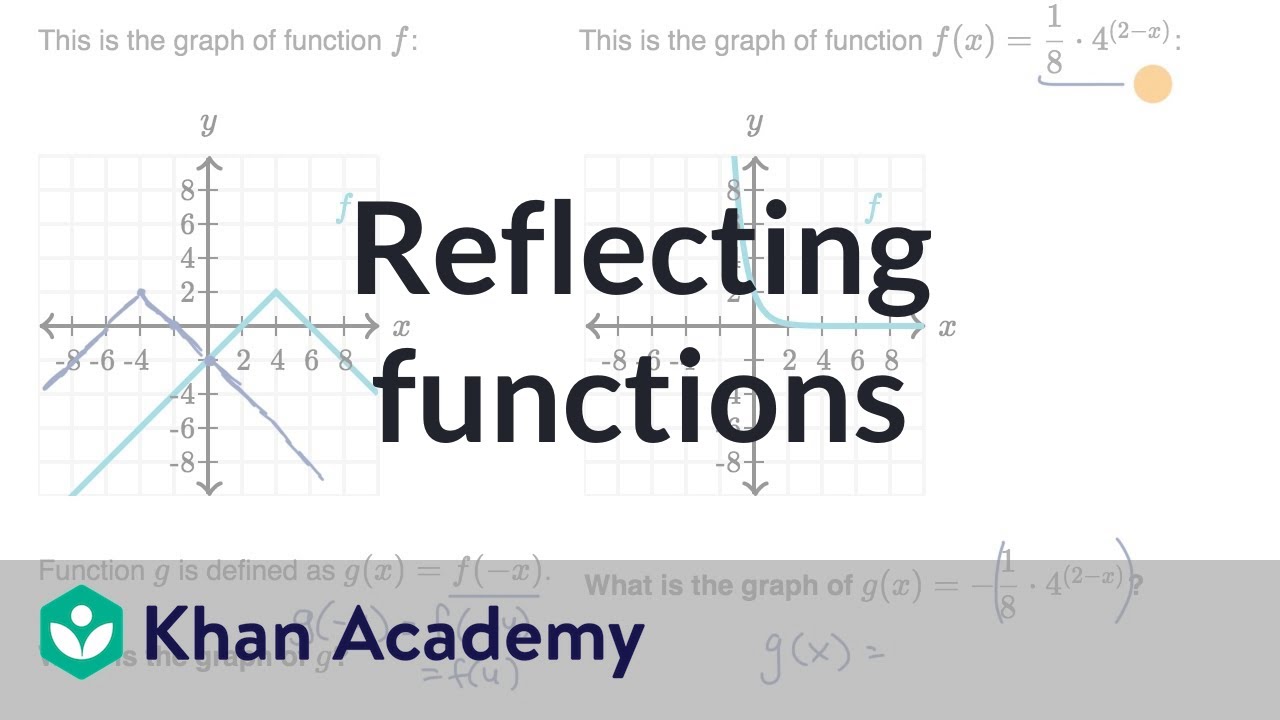
Reflecting Functions Examples Video Khan Academy

The Transformation Of The Graph Of A Quadratic Equation Matherudition

Reflections And Symmetry

Transformation Of Graphs Highschool Learnmath

Function Transformations
2
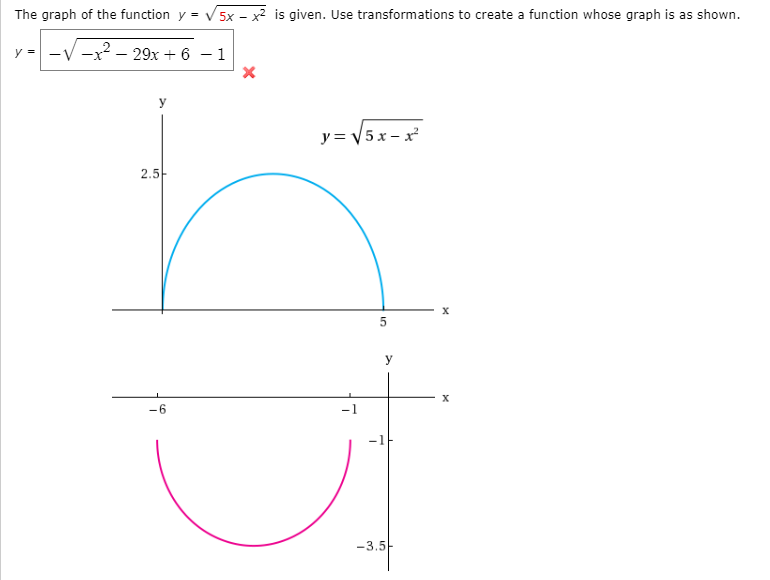
Answered The Graph Of The Function Y V 5x X Bartleby

14 More About Graphs Of Functions Transformation Effectively How To Memorise The Graphs Of Functions After O Y X A Translate The Graph Of Y F X K Ppt Download

Transformations Left Or Right
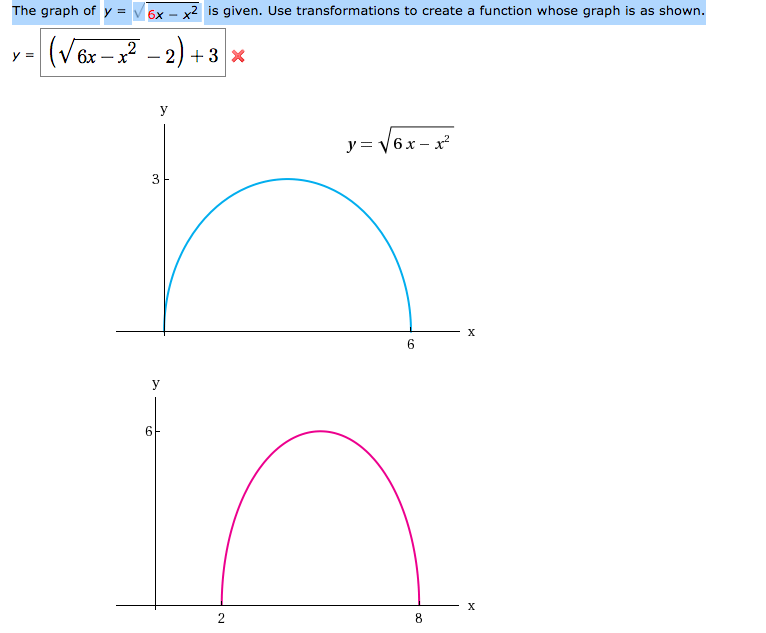
Solved The Graph Of Y Squareroot 6x X 2 Is Given Use Chegg Com

Combining Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation

How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 8 And Describe The Transformation Homeworklib
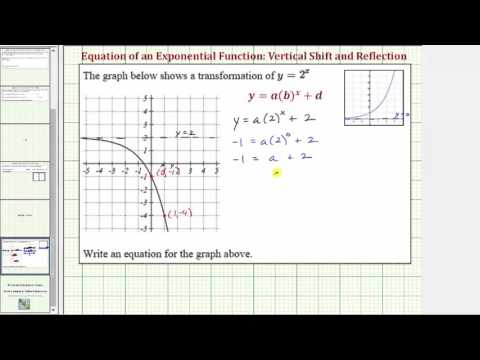
Ex Determine The Equation Of A Transformation Of Y 2 X Youtube
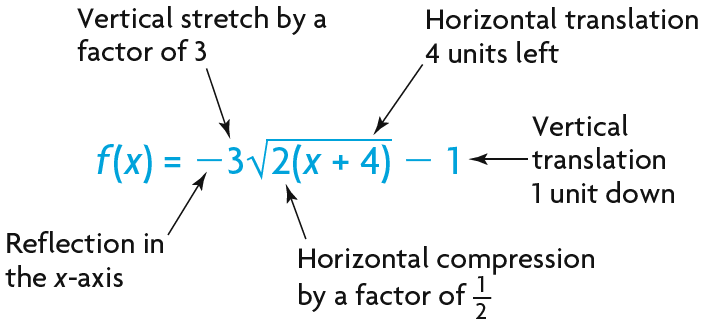
Using Transformations To Graph Functions Of The Form
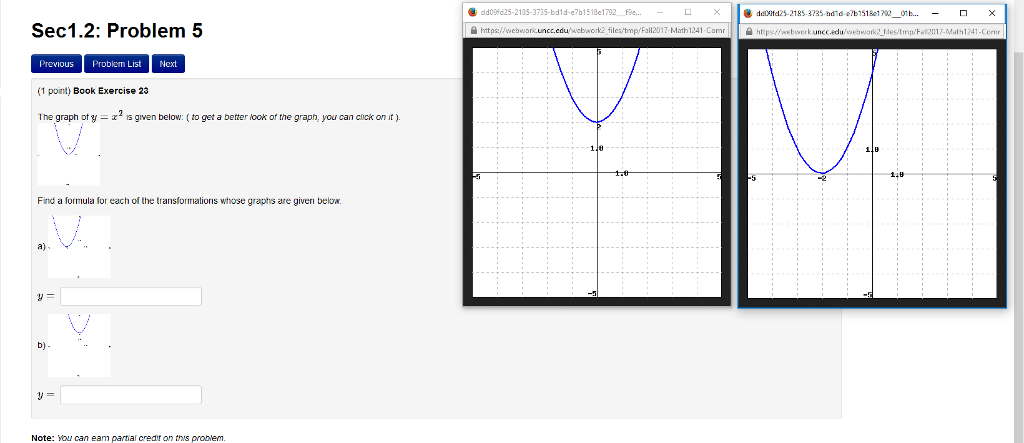
Solved The Graph Of Y X 2 Is Given Below To Get A Bet Chegg Com
Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
Solved 1 Point The Graph Of Y X2 Is Given Below 10 T Chegg Com
Sequence Of Transformations On Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math

2 5 Transformations Of Functions Pdf Free Download
Using Transformations To Graph Functions
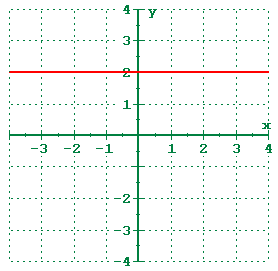
1 5 Shifting Reflecting And Stretching Graphs
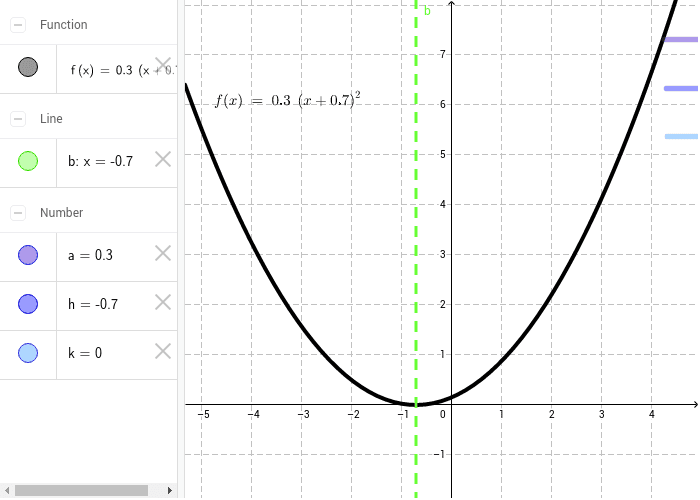
Transformations To The Graph Of Y X 2 Geogebra
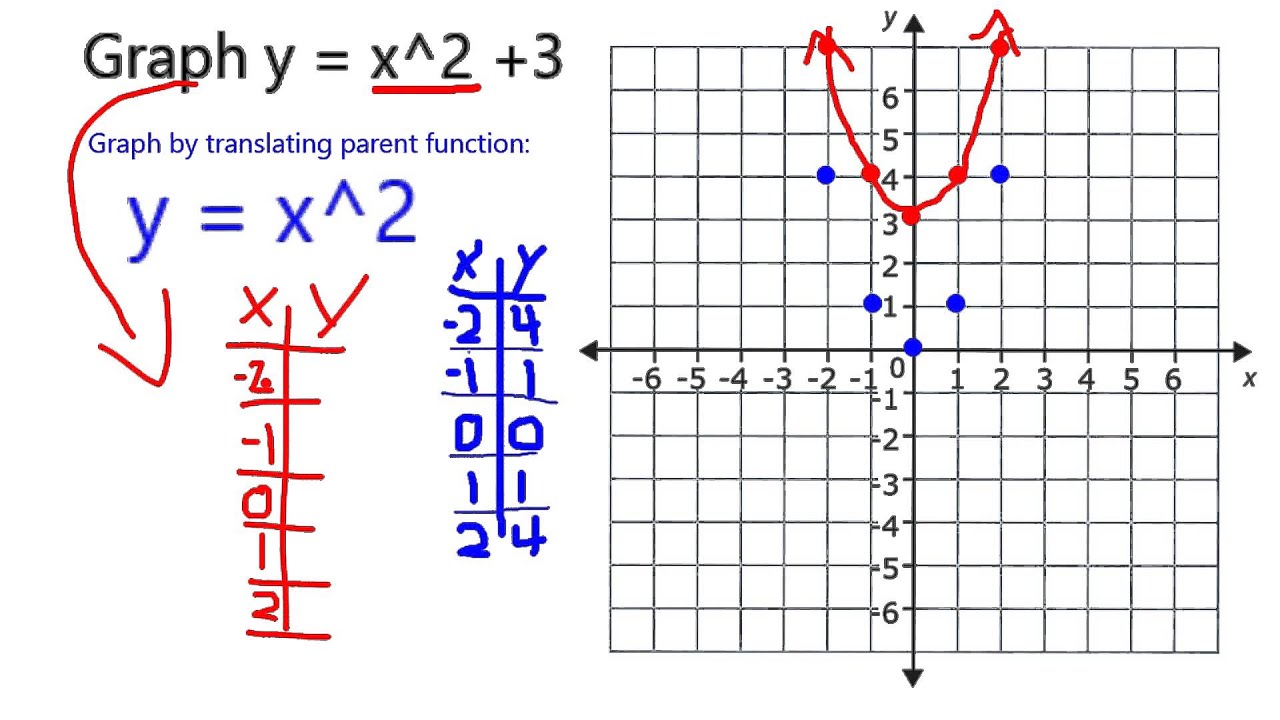
Graph Y X 2 3 Youtube
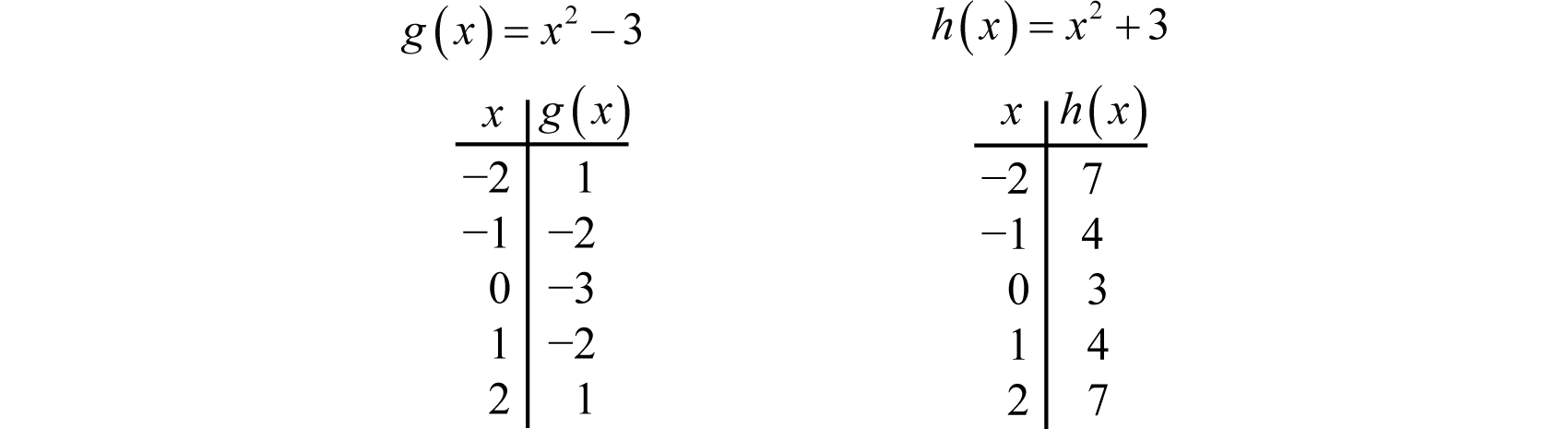
Using Transformations To Graph Functions

Translations Of A Graph Topics In Precalculus
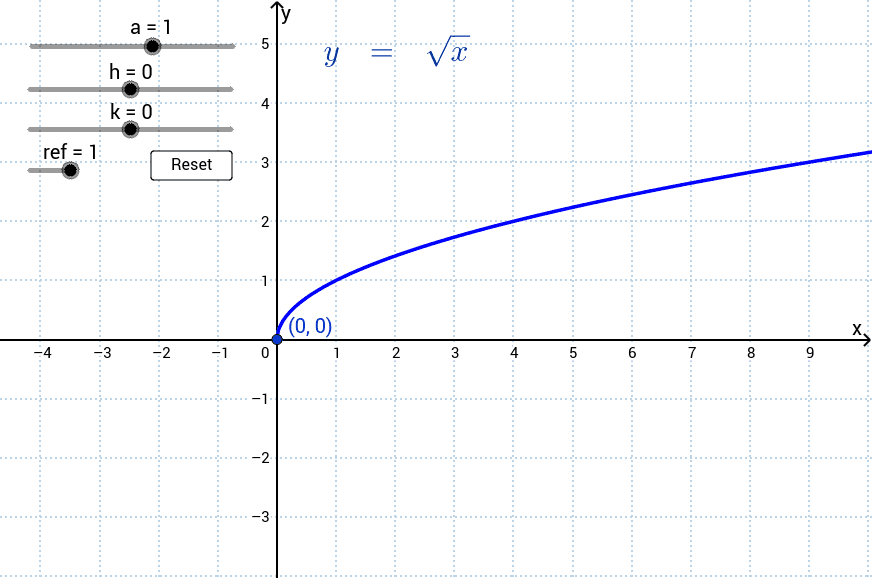
Transformations Of The Graph Y Sqrt X Geogebra

Graphing Shifted Functions Video Khan Academy

The Graph Of Y Sqrt 4x X 2 Is Given Below Use Transformations To Create A Function Whose Graph Is As Shown Below Study Com
Gregory Jaczko Transformations Of Graphs
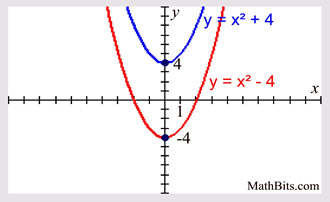
Parabola Parent Function Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
Describe The Geometrical Transformation That Maps The Graph Of Y X 2 Onto The Graph Of Y X 2 2x 5 Enotes
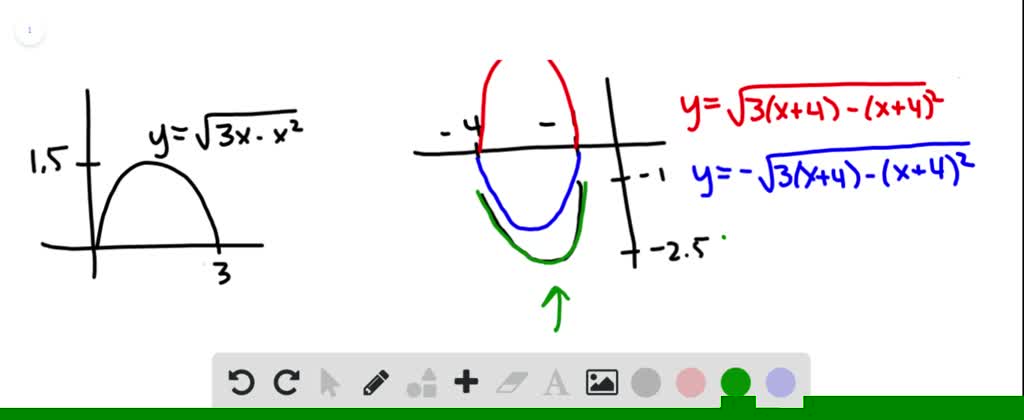
The Graph Of Y Sqrt 3x X 2 Is Given Use Tr

Parabola Transformations Match Up 1 Distance Learning High School Mathematics Quadratics Quadratic Functions

Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
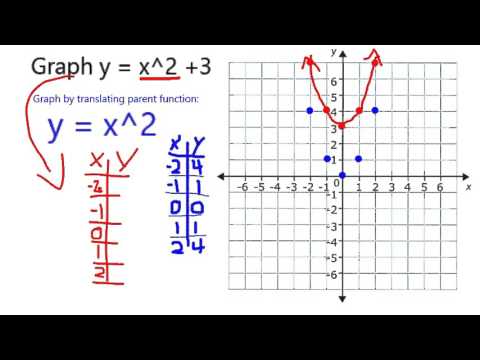
Graph Y X 2 3 Youtube
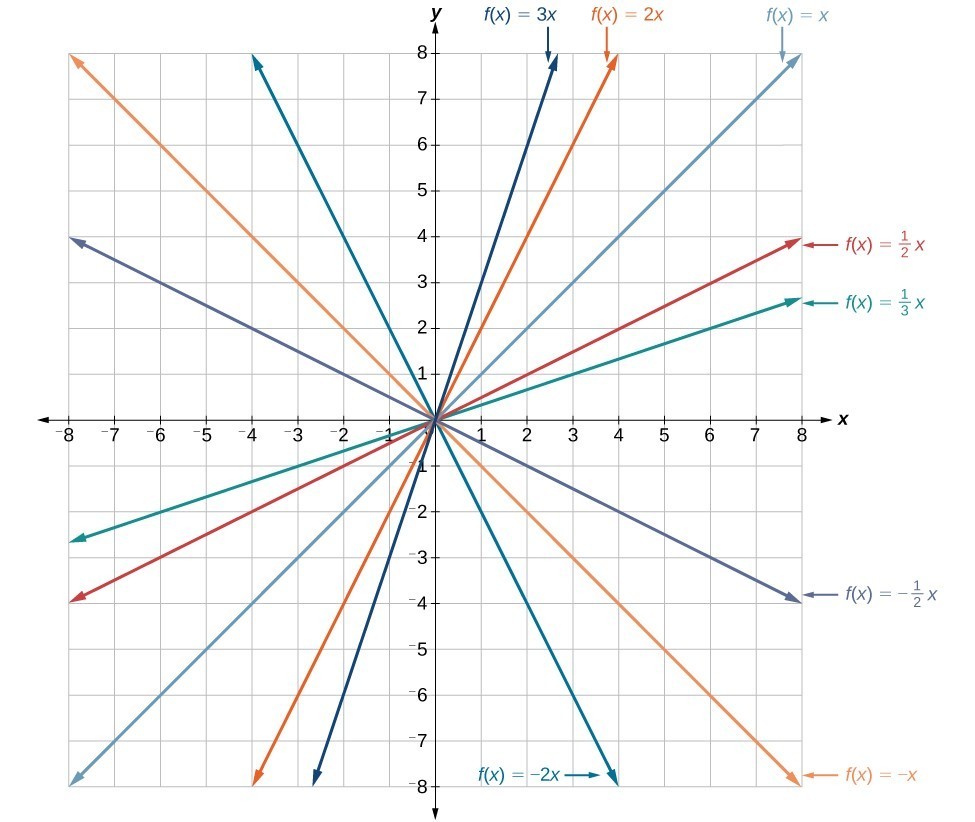
Read Transform Linear Functions Intermediate Algebra

Transformations Of Quadratic Functions The Translations Dilations And Reflections
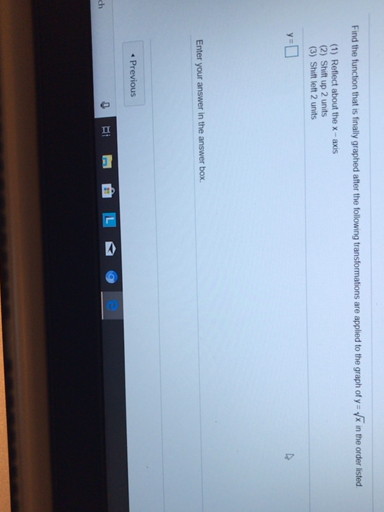
Find The Function That Is Finally Graphed After The Following Transformations Are Applied To The Graph Of Math Y Sqrt X Math In The Order Listed 1 Reflect About The X Axis 2 Shift Up 2 Units
Q Tbn 3aand9gctqxpc0pjtnfm1m54ybsslvdpzttnnxzztapn5jahvkruyfh8sw Usqp Cau
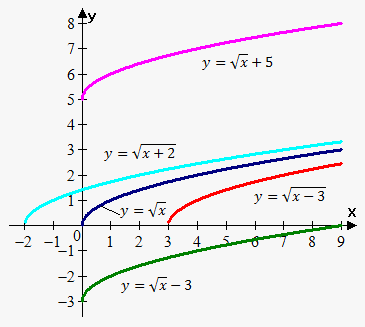
Transformation Of Functions On Emathhelp

1 I Describe The Transformation That Maps Graph P To Each Of The

Transforming Exponential Graphs Example 2 Video Khan Academy

The Transformation Of The Graph Of A Quadratic Equation Matherudition
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqy2alsdvfj5tbhwq1cfn1ccupteisepapiscfaxn2p2jp5odws Usqp Cau

Consider The Graph Given Below Determine Which Sequences Of Transformations Could Be Applied To The Brainly Com
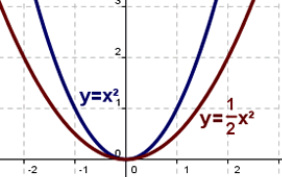
Transformations Mrs F X
Quadratic Transformations Part 1 Activity Builder By Desmos

Sec 2 4 Transformation Of Graphs Copyright C By Houghton Mifflin Company Inc All Rights Reserved 2 The Graphs Of Many Functions Are Transformations Ppt Download
How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2 2 And Describe The Transformation Socratic
Parent Functions And Their Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
What Is A Function Transformation Expii
Transformations Boundless Algebra
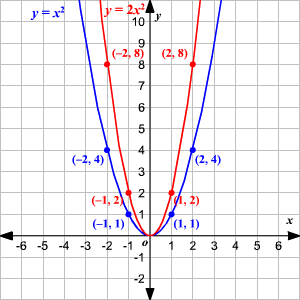
Graphing Quadratic Equations Using Transformations

Content Transformations Of The Parabola
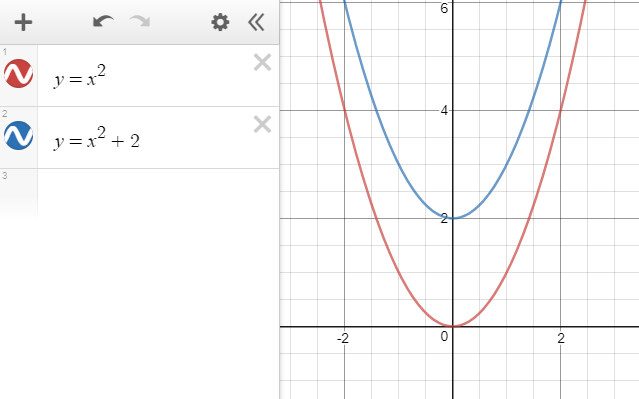
Desmos 2 Transformations Of Graphs Cambridge Maths Hub
Solution I Have A Question That States A Use The Transformations On The Graph Of Y X 2 To Determine The Graph Of Y X 5 2 9 B Using The Graph Of F X X 2 As A Guide Graph

The Graph Of Y Sqrt 8x X 2 Is Given Use Transformations To Create A Function Whose Graph Is As Shown Study Com
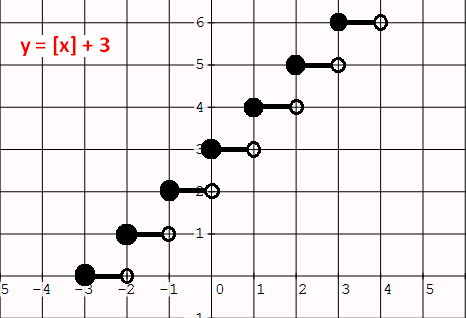
Graphing Greatest Integer Function

Transformations Of Functions Ck 12 Foundation
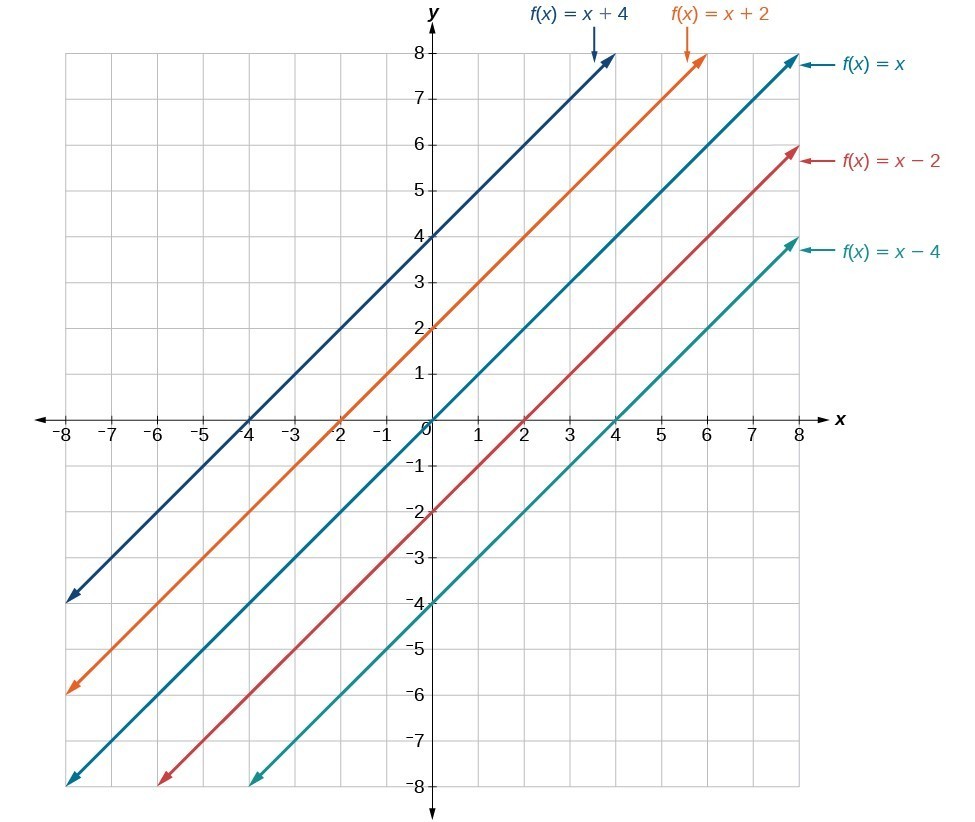
Read Transform Linear Functions Intermediate Algebra

Transformations Up Or Down

Vertical Shifts Let C Represent A Positive Number How The Function Is
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr8k8gbgd5dq1m1crviuff8o0l6unfp3gluelz3vkyooxhkupfs Usqp Cau

Transformations Of Quadratic Functions The Translations Dilations And Reflections

Stretching And Reflecting Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation
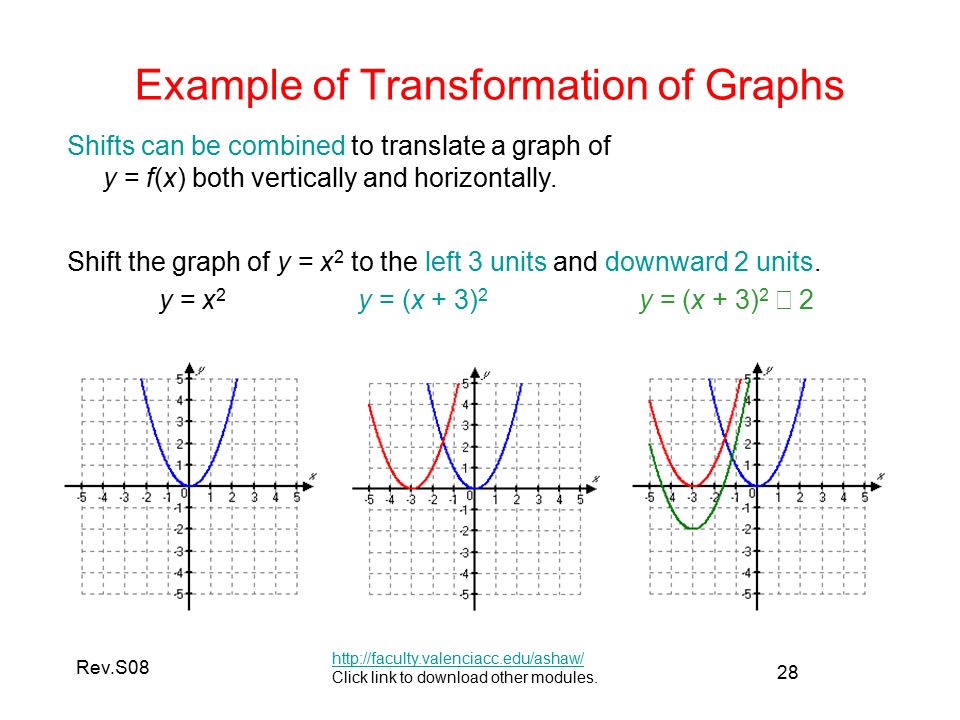
Transformation Of Graphs Ppt Video Online Download

Describe The Transformations Of The Graph Of Y X That Will Produce The Graph Of Y X 2 2 3 Brainly Com

Content Transformations Of The Parabola

Vce School Notes Graph Transformations
Q Tbn 3aand9gcslmi2imnz5wskjyszusujbqila Bvuhtgst6wsfbs8tfgbswdf Usqp Cau
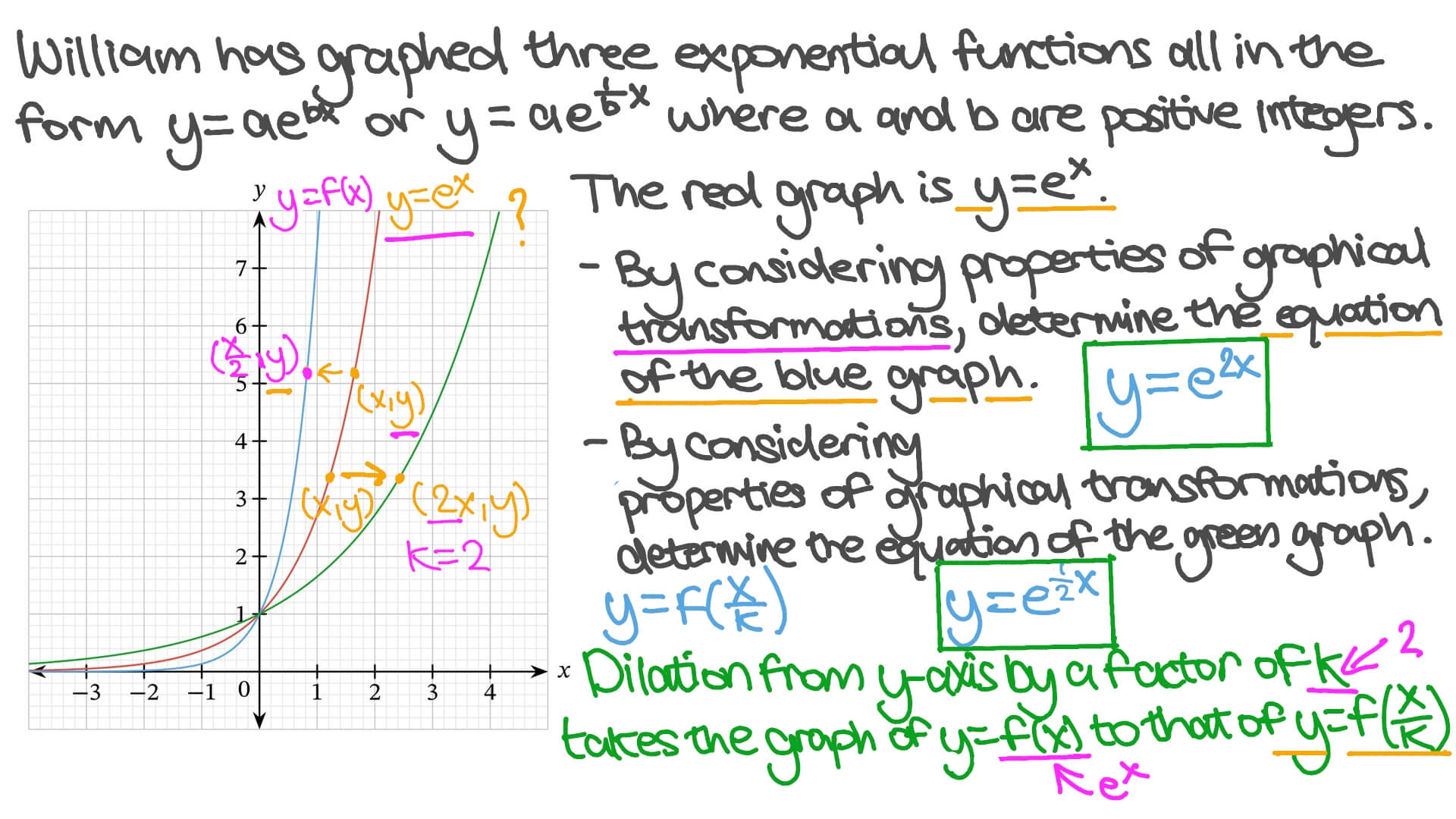
Video Graph Transformations Of Exponential Functions Nagwa

Transformations Of Quadratics
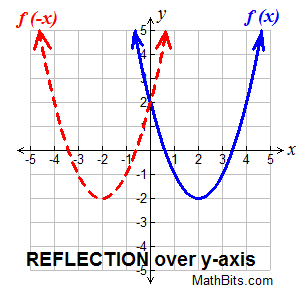
Transformations Of Functions Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math
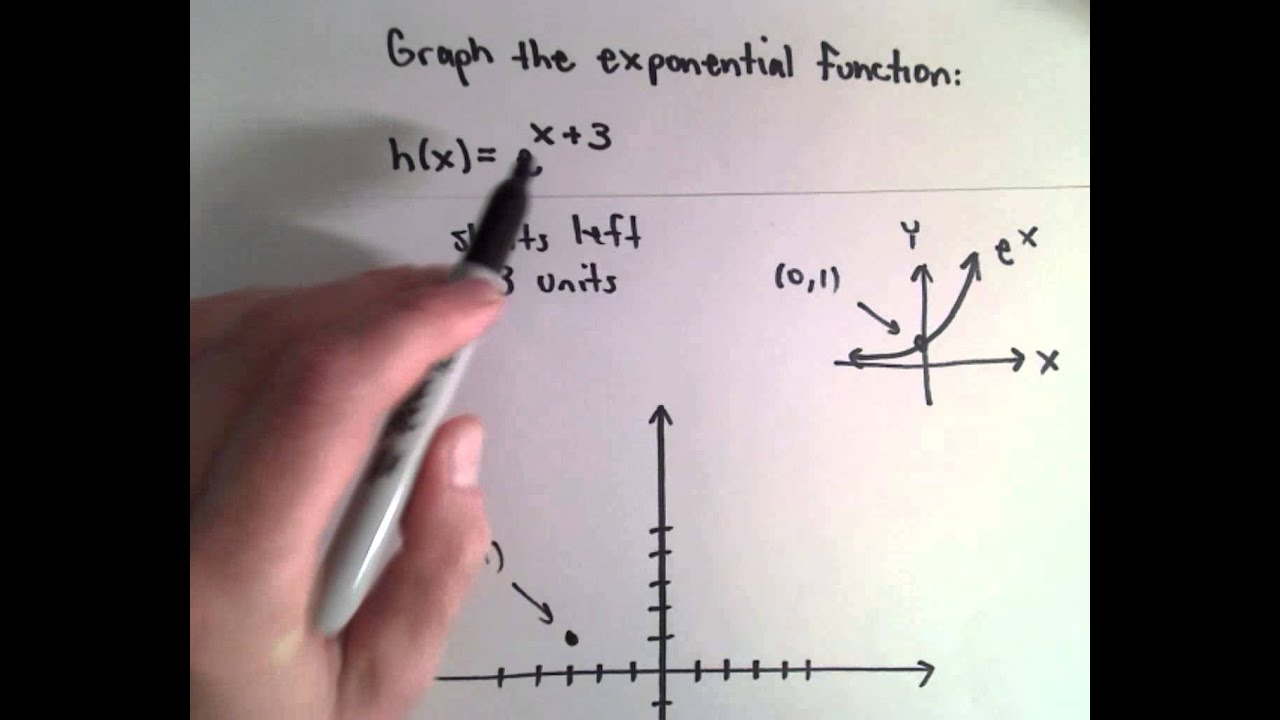
Graph Of Y E X 3 Using Graph Transformations Youtube

The Graph Of Y Sqrt 8x X 2 Is Given Use Transformations To Create A Function Whose Graph Outlines The Figure Shown Study Com
Transforming Exponential Graphs Example 2 Video Khan Academy

Graphs Of Quadratic Function Introducing The Concept Transformation Of The Graph Of Y X Ppt Download

Transforming Graphs Of Functions Brilliant Math Science Wiki

Compress Or Stretch Function Horizontally F Cx Expii

Content Geometric Transformations Of Graphs Of Functions
Solved If You Compare The Graph Of Y X2 3 To The Graph Of Chegg Com

Amazon Com Transformation Of Graphs Math Posters For Common Core State Standards Ccss Gloss Paper 33 X 23 5 Math Charts For The Classroom Education Charts By Daydream Education Industrial Scientific

Content Transformations Of The Parabola
How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 3 2 6 And Describe The Transformation Socratic

Discovering Advanced Algebra Resources
Transformations Of Graphs

The Graph Of The Function Y Sqrt 3x X 2 Is Given Use Transformations To Create A Function Whose Graph Is As Shown Study Com
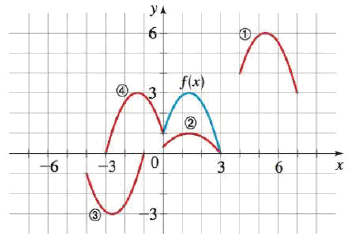
Identifying Transformations The Graph Of Y F X Is Given Match Each Equation With Its Graph 70 A Y 1 3 F X B Y
Trasformations By Graph Paper Activity Builder By Desmos

Symmetry Transformations And Compositions
The Graph Of The F X Is Show Below Graph Each Transformed Function And List In Words The Transformation Used Socratic

Reflections And Symmetry
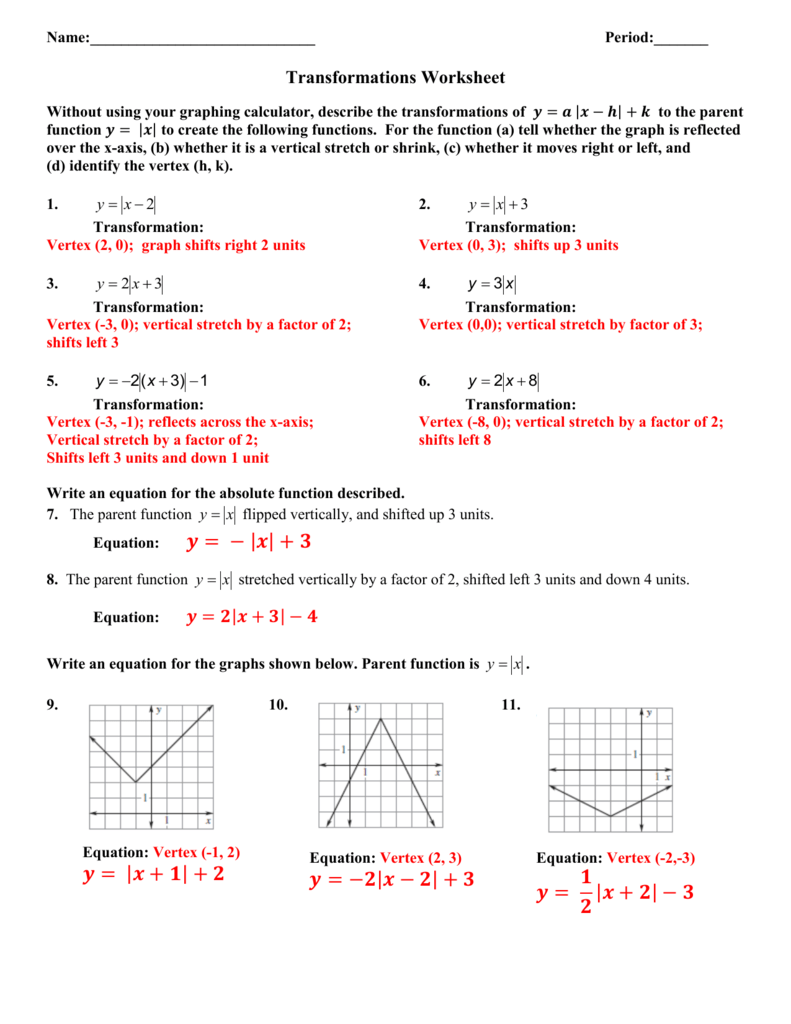
Absolute Value Transformations

Graph Transformations Muic Math
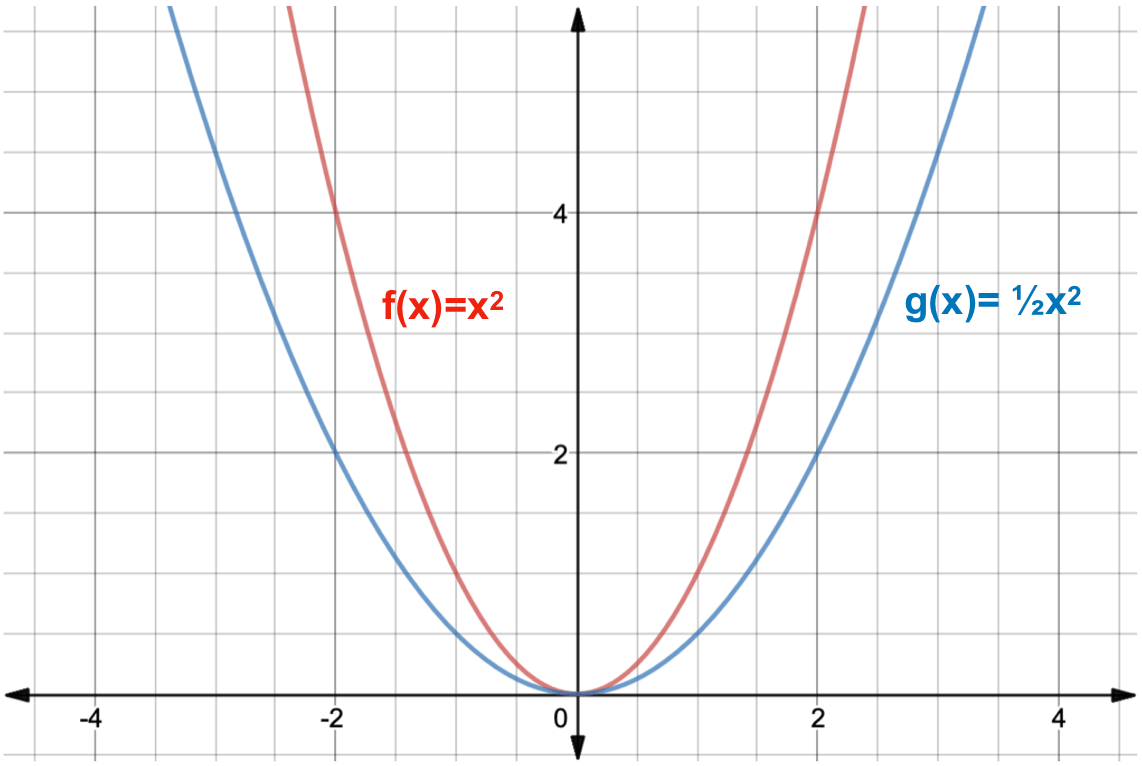
What Is A Function Transformation Expii




